Tide’s Secure Web Enclave
Tide’s Secure Web Enclave (SWE) is a browser‑delivered, verifiable JavaScript module that serves as the untrusted dealer for all end‑user cryptographic operations-authentication, encryption, decryption, signing, and more. It orchestrates the Multi‑Party Computation (sMPC) flows against the Tide Cybersecurity Fabric and ensures neither the client nor any network node can be corrupted without detection.
Why SWE?
Traditional web front‑ends require blind trust in the vendor. SWE replaces that with provable integrity: every byte of the enclave bundle is integrity‑checked in the browser via Subresource Integrity (SRI), and its sMPC interactions are anchored in zero‑knowledge proofs, quorum voting, and a Merkle‑anchored state ledger.
Background
When a platform goes into production, attackers only need a single breach point. Tide flips this model: even if infrastructure is compromised, no attacker can reconstruct full key material. SWE delivers that guarantee directly to the user’s browser.
How SWE Works
-
Code Delivery & Verification
- SWE is served as a signed HTML/JS/WASM bundle with a pinned SHA‑256 SRI hash.
- Browsers refuse to run the enclave if its bundle is tampered.
- Users can fetch the official SRI hash from Tide’s Integrity Checker.
-
Session Initialization
- User enters credentials in SWE.
- SWE blinds inputs (password, 2FA) into zero‑knowledge proofs (PRISM protocol).
-
sMPC Orchestration
- SWE selects Fabric nodes via the TWELVE‑MAP directory.
- Nodes compute partial shares (Encrypt, Decrypt, Sign, Authenticate).
- SWE aggregates ≥ 14 out of 20 shares, verifies ZK proofs, and completes the action.
-
Result Delivery
- No secret ever exists in one place-only distributed shares.
- SWE presents the final ciphertext, signature, or token to the calling application.
Where SWE Fits
User Browser → SWE (dealer) → Fabric nodes → ZK proofs → SWE → App backend
- SWE is the only code on the client that touches user credentials.
- All coordination and cryptography happen in flight, with no HSMs or TEEs required.
Provable Front‑End Integrity
HTML structure guarantees (inline code):
- A single
<html>…</html>wrapper - A single empty
<body></body>block - A single
<head>containing exactly one<script>tag - That
<script>has only:defer,src,integrity, andcrossoriginattributes
<html>
<head>
<script defer src="..." integrity="sha256-..." crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
If any bit of this bundle changes, the browser refuses to execute it-and SWE won’t start.
Steps to Validate SWE Locally
-
Load the Enclave
Navigate to your platform’s sign‑in page and open the SWE (e.g., via your federated‑login button).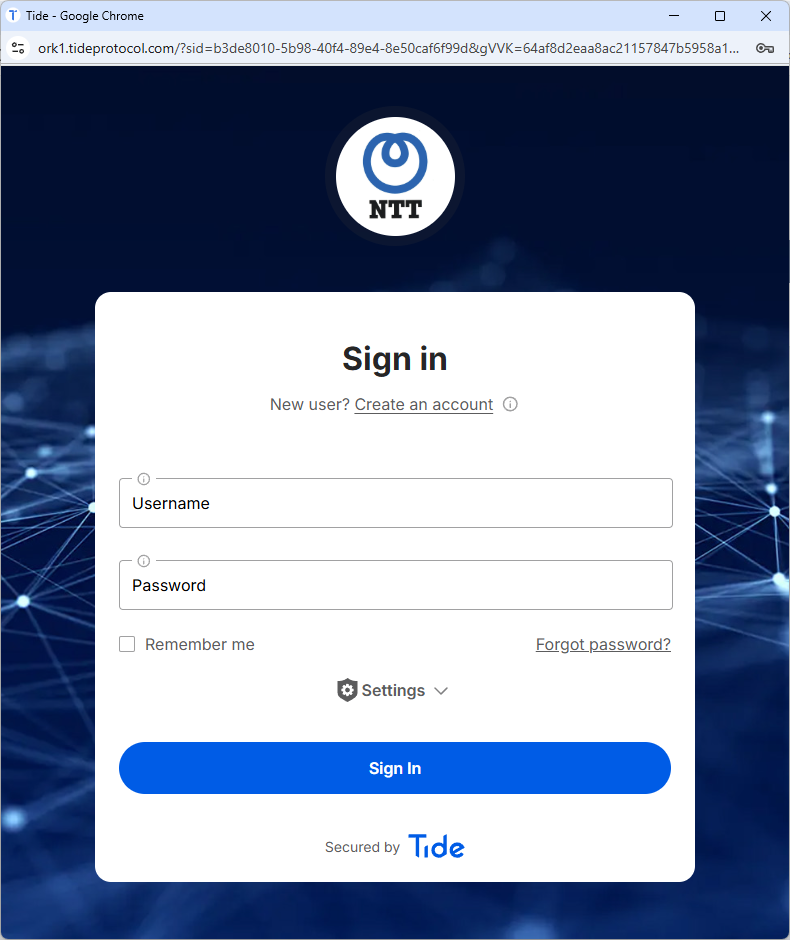
-
View Page Source
Right‑click and select View Page Source. Confirm you see the minimal HTML above (no extra tags).
-
Extract & Verify the SRI Hash
- Copy the
integrityattribute value from the<script>tag. - Open Tide’s Integrity Checker and paste the hash.
- A VALID response means your enclave matches the audited bundle.
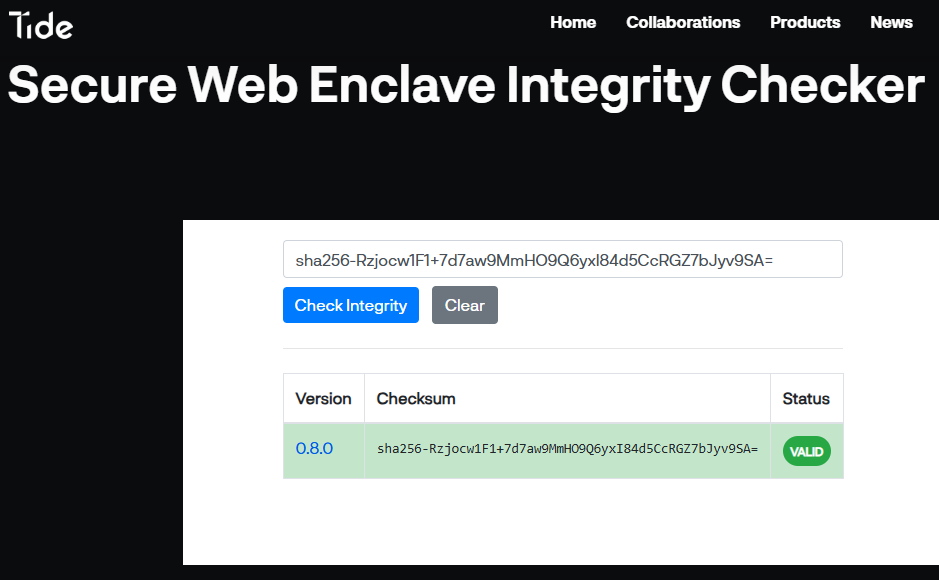
- Copy the
-
Optional: Rehome the Enclave
If you need to serve SWE from your own origin (S3, on‑prem), click Settings → Switch Sign‑In Host and enter your custom URL. The same SRI hash applies, so security remains intact.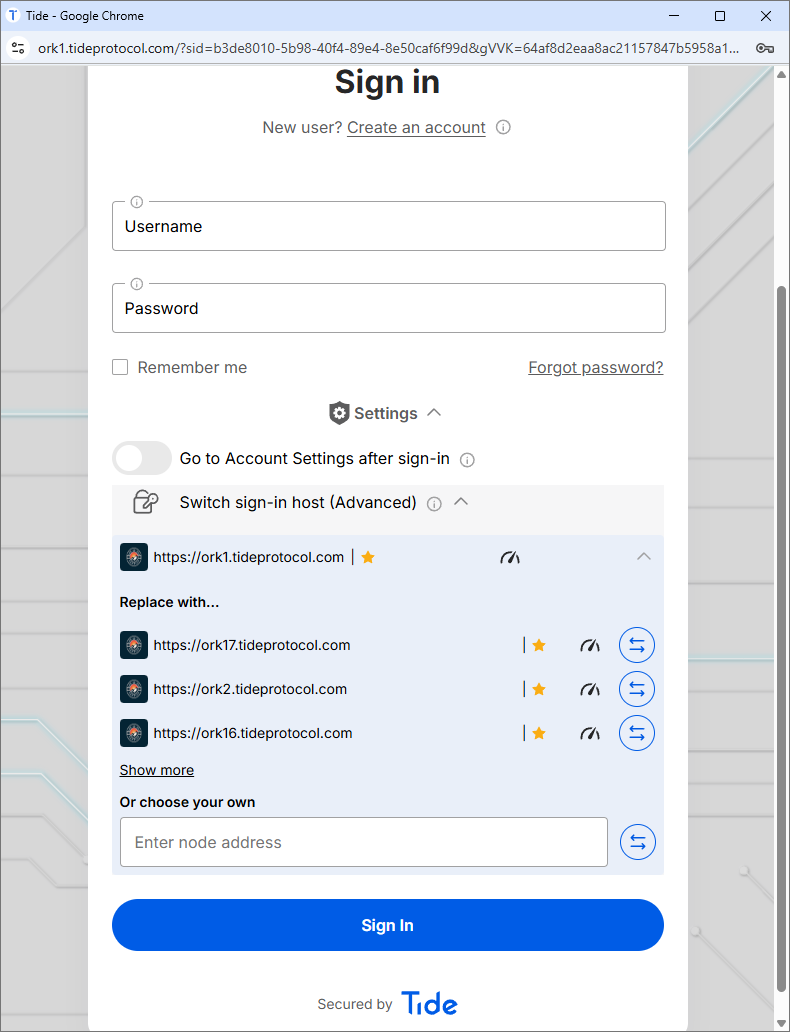
Developer Benefits
- No Secret Glue Code: Remove custom HSM integrations; just import SWE as a script.
- Instant Trust Audits: Every build and CI pipeline can verify the same SRI hash.
- Zero‑Trust Everywhere: The front‑end is now part of the cryptographic trust fabric.
Next Steps
- Integrate SWE via our NextJS SDK.
- Read more about PRISM & sMPC protocols.